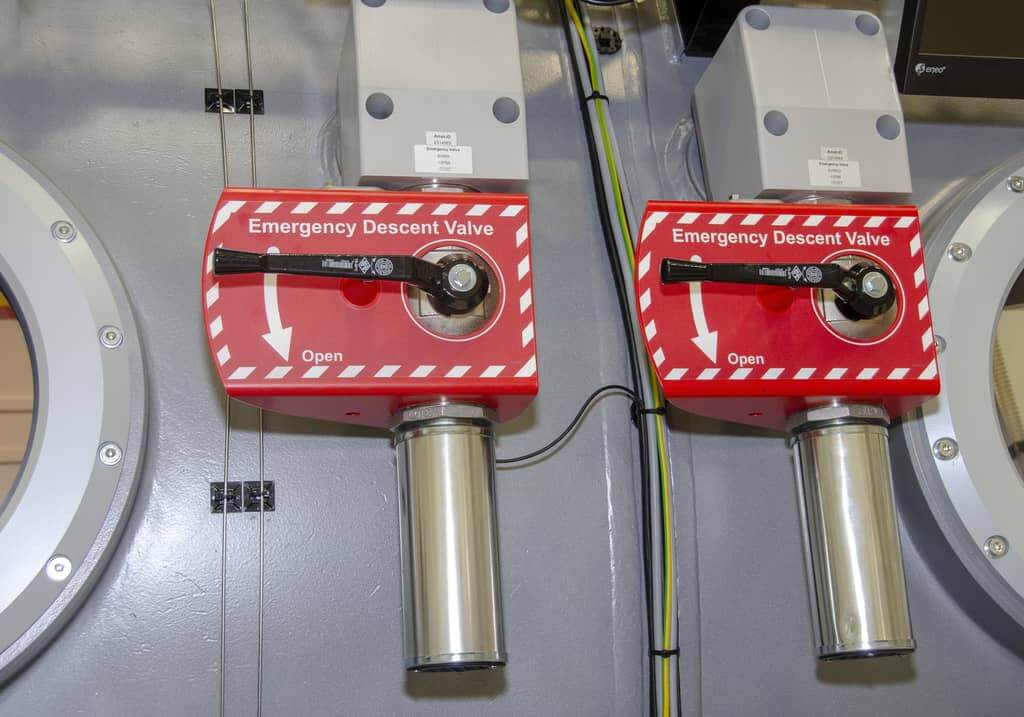
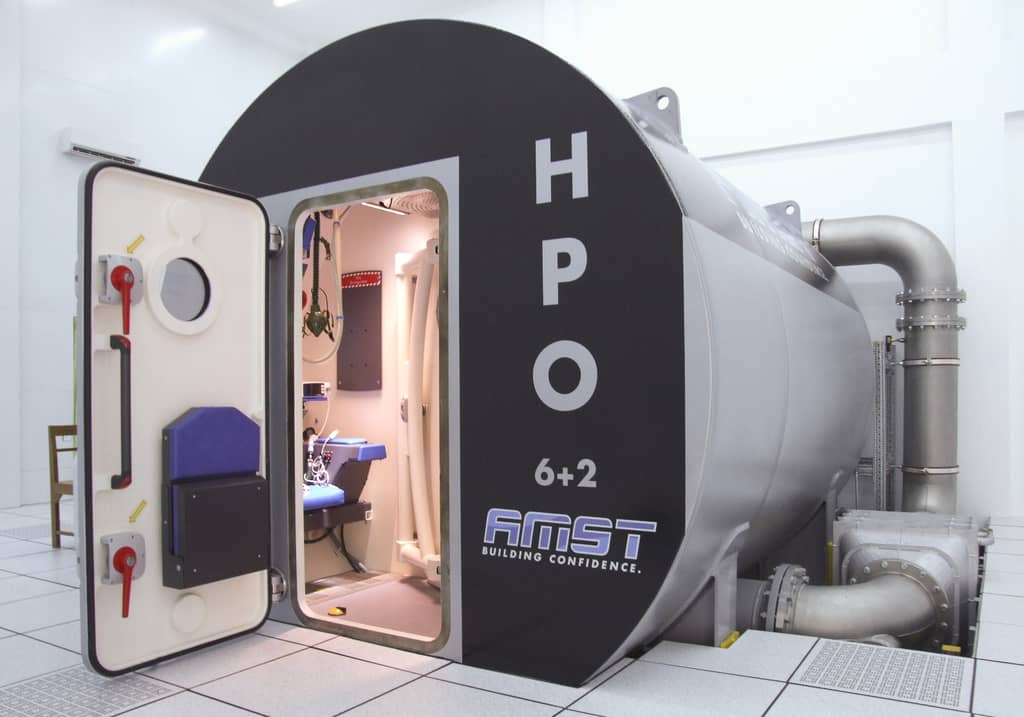
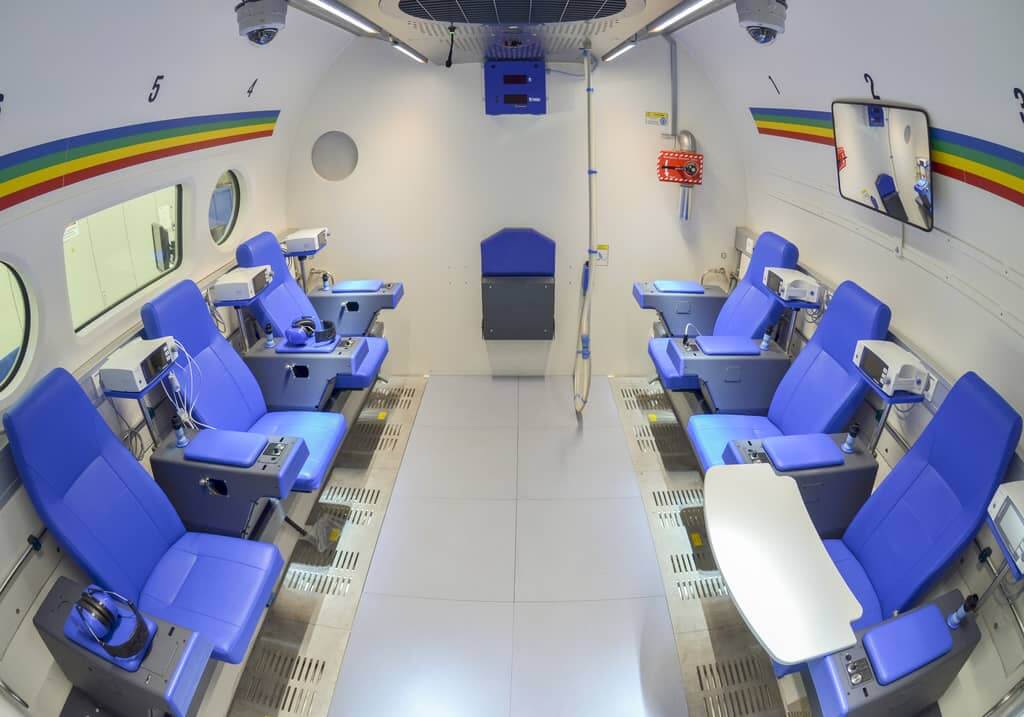
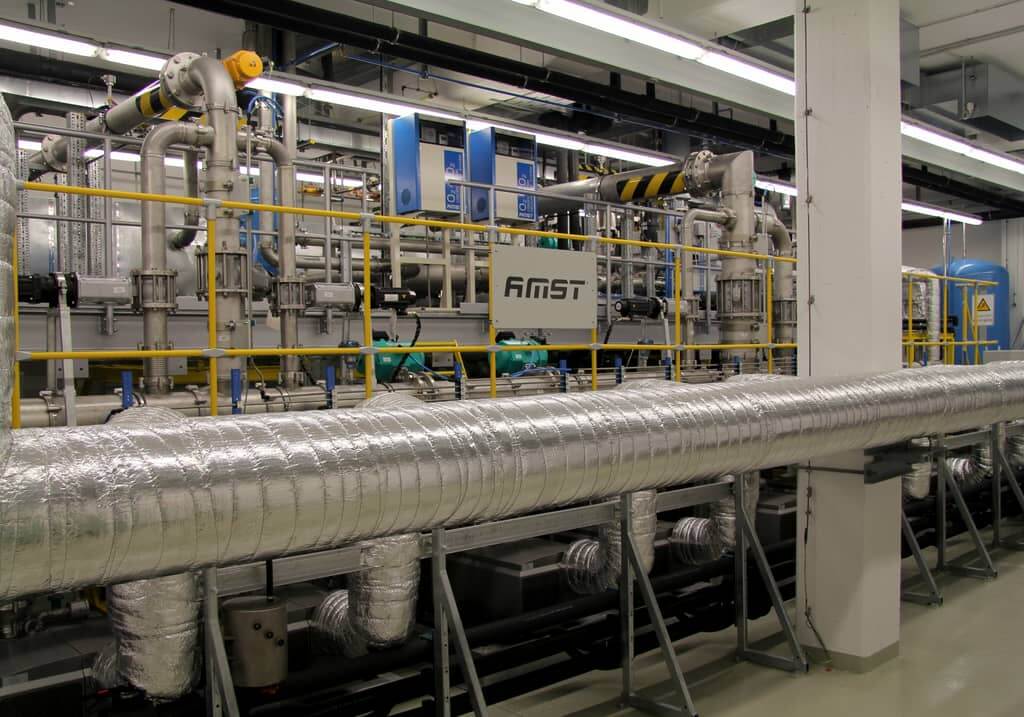
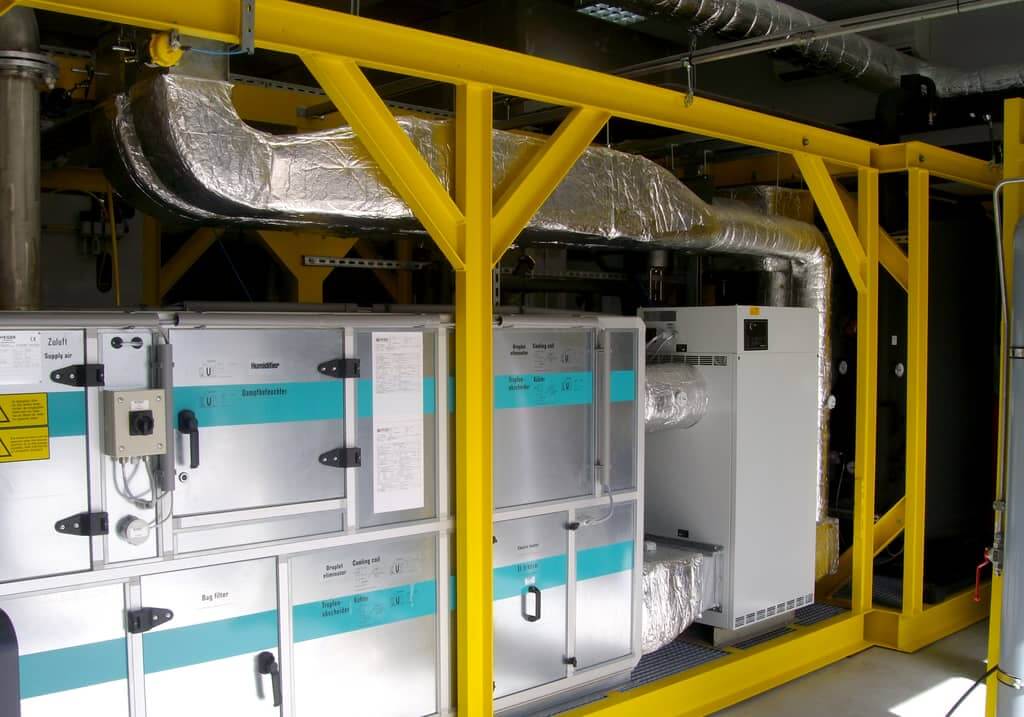
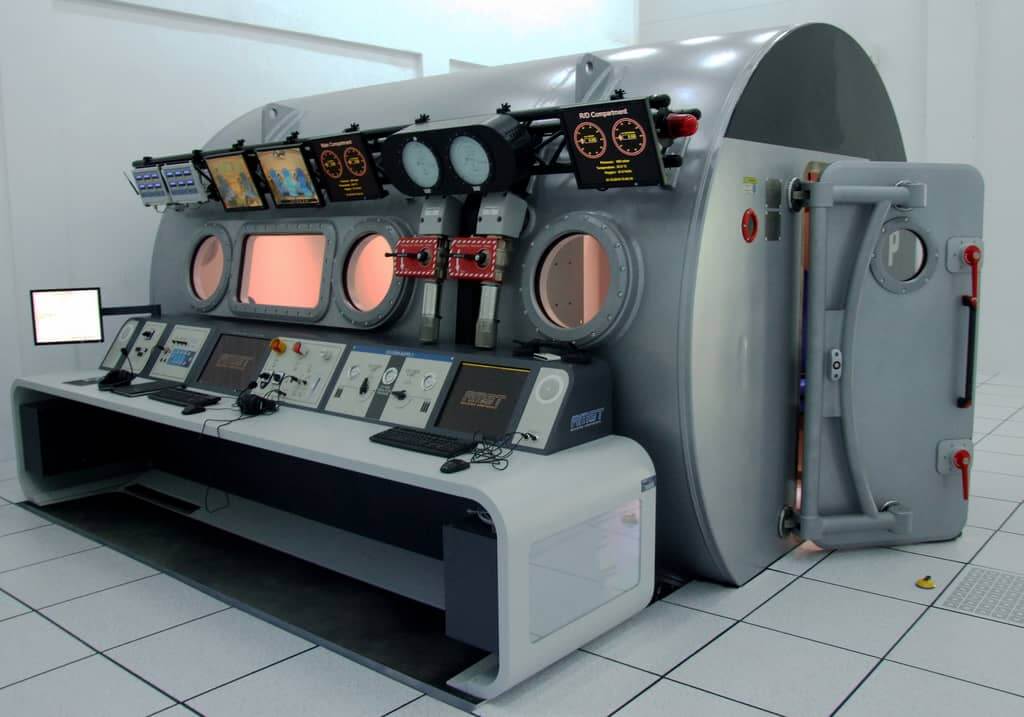
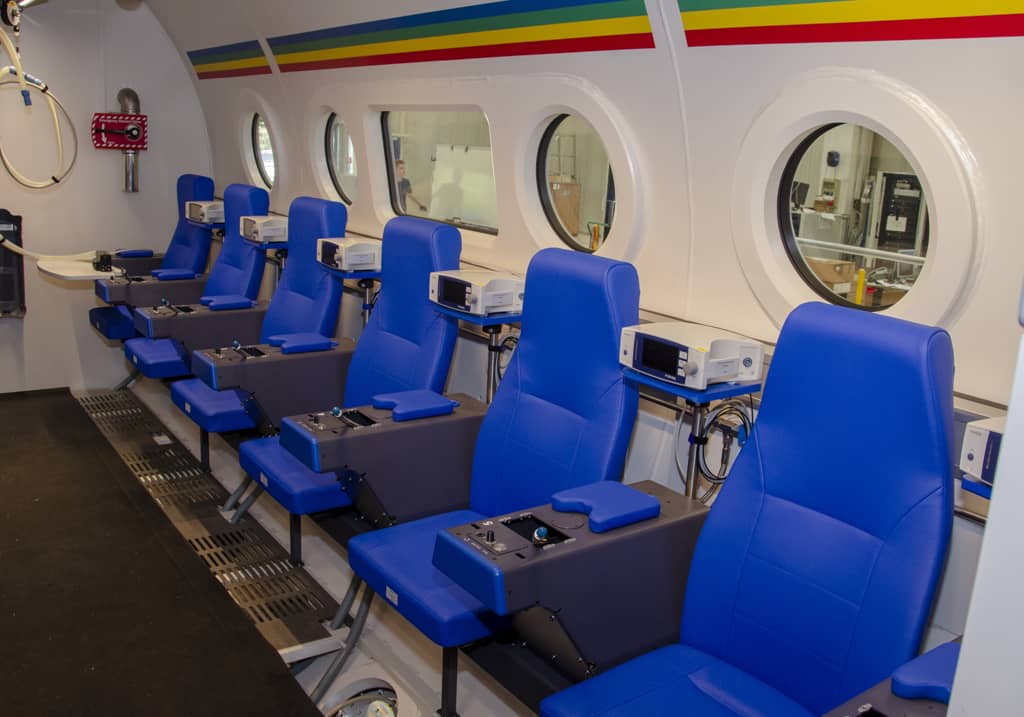
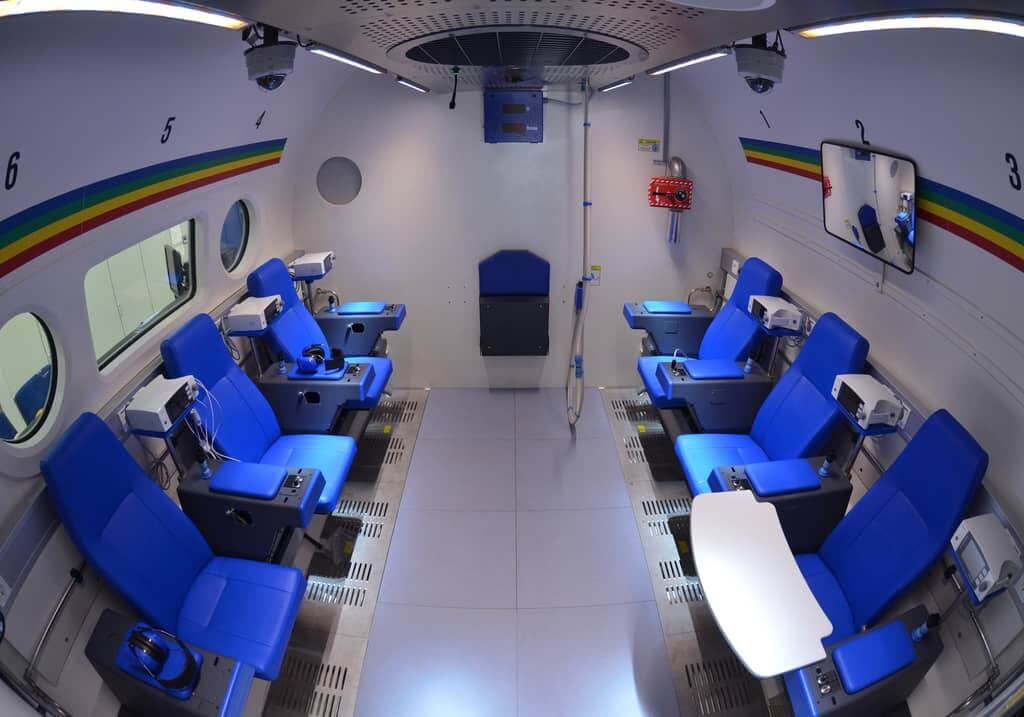
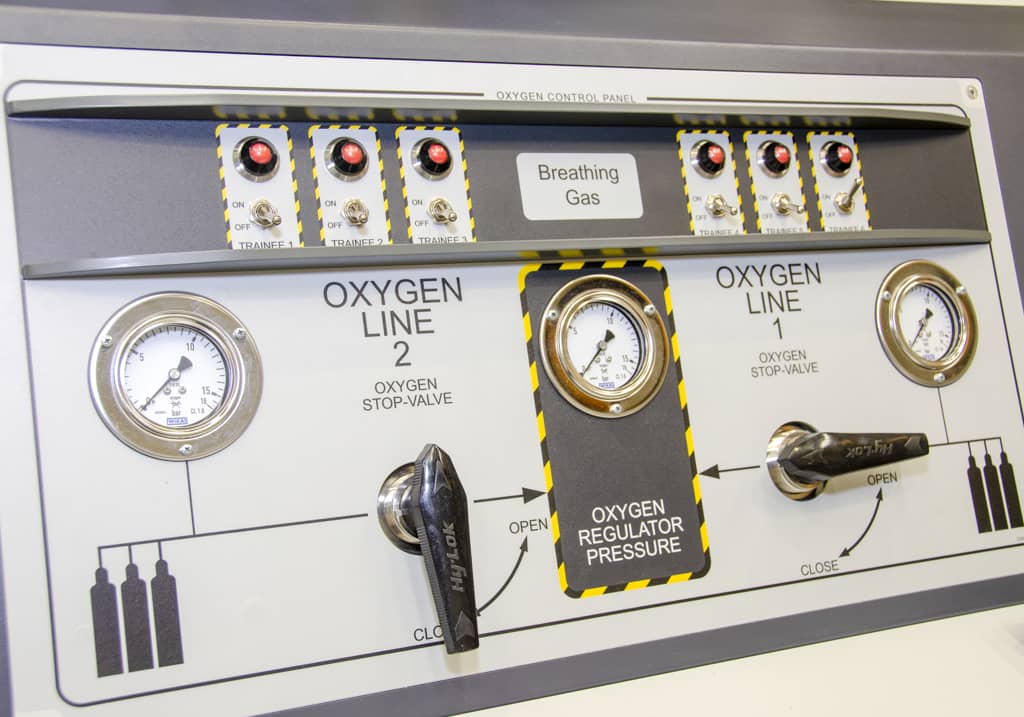
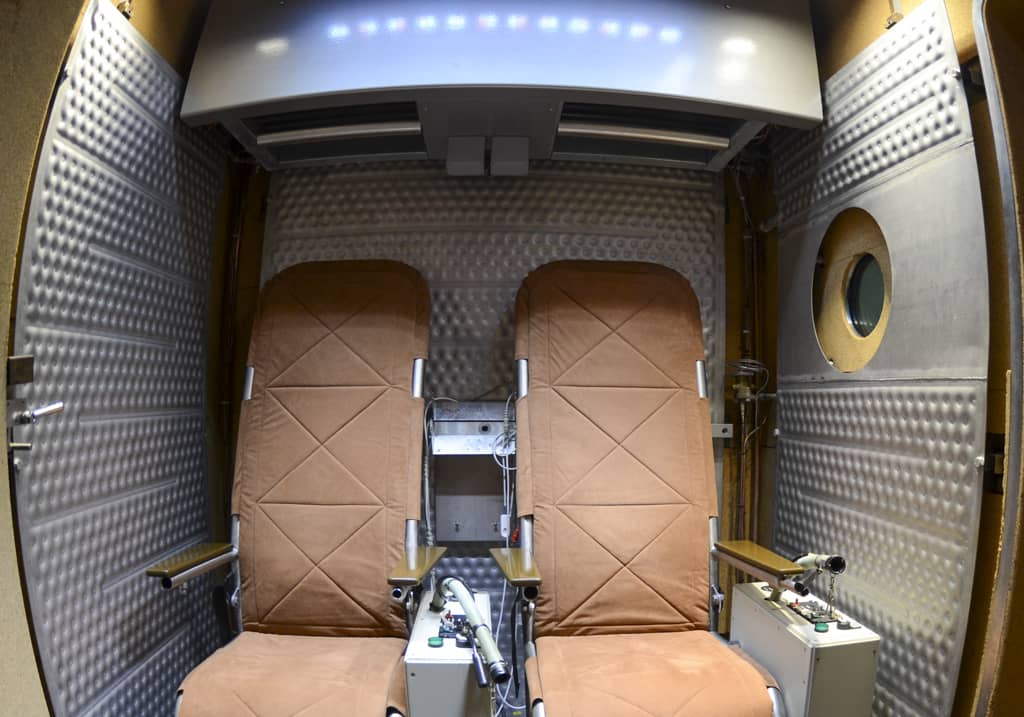
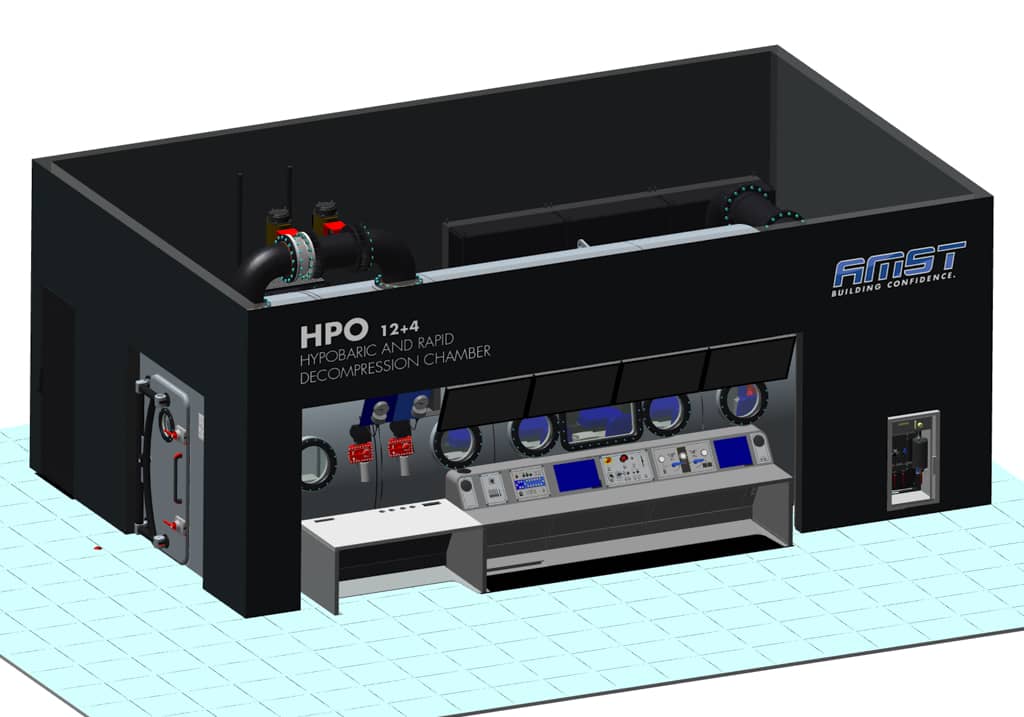
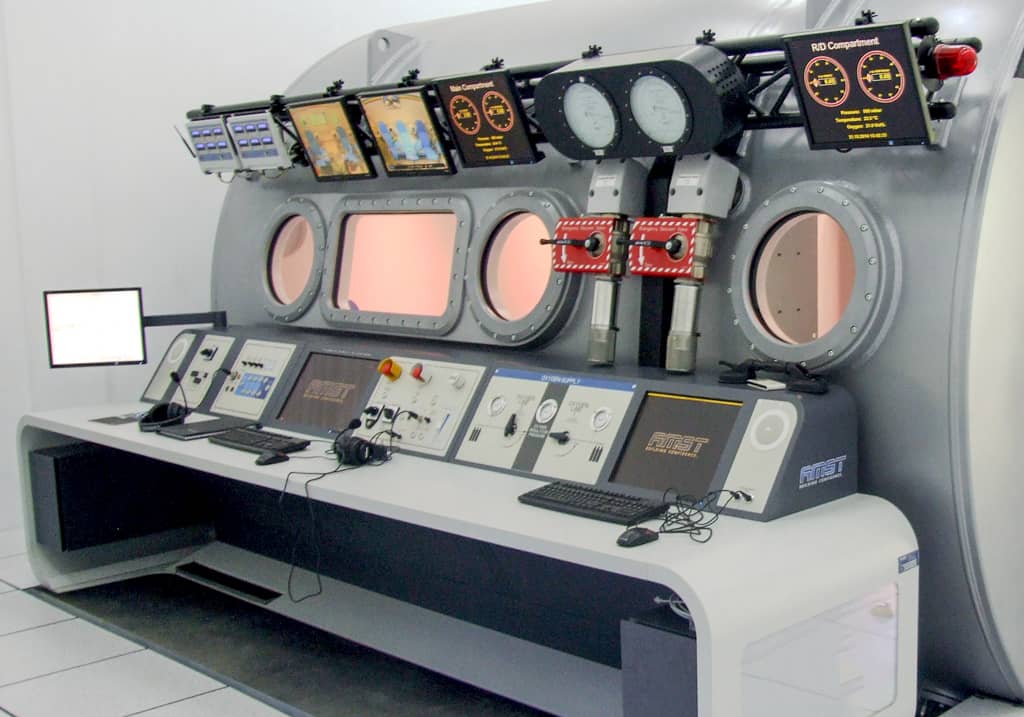
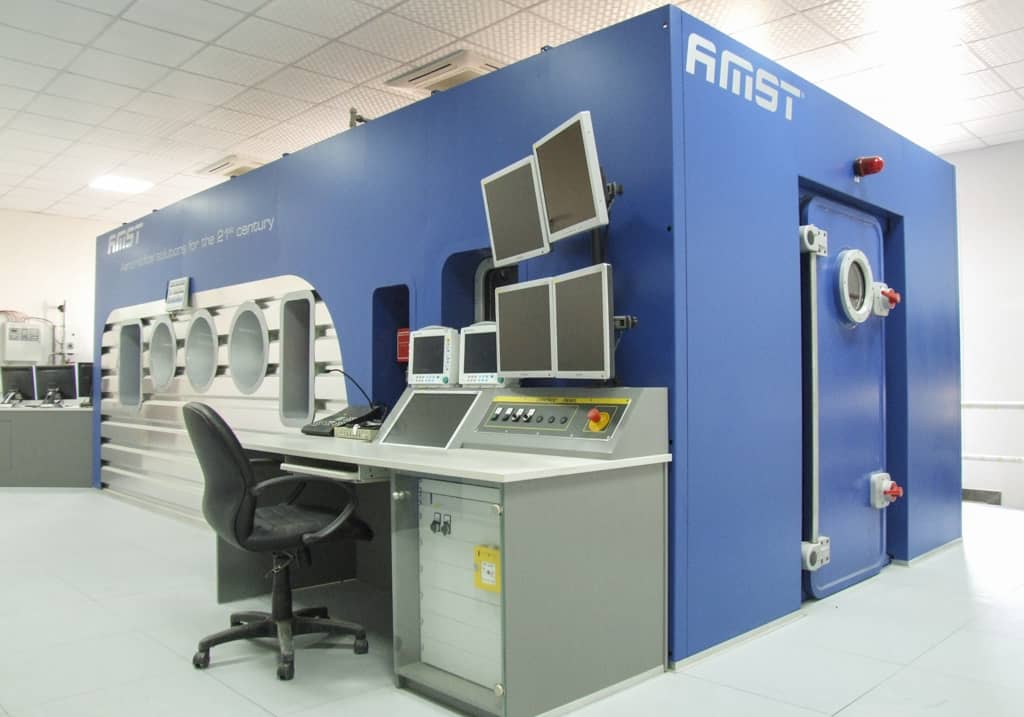
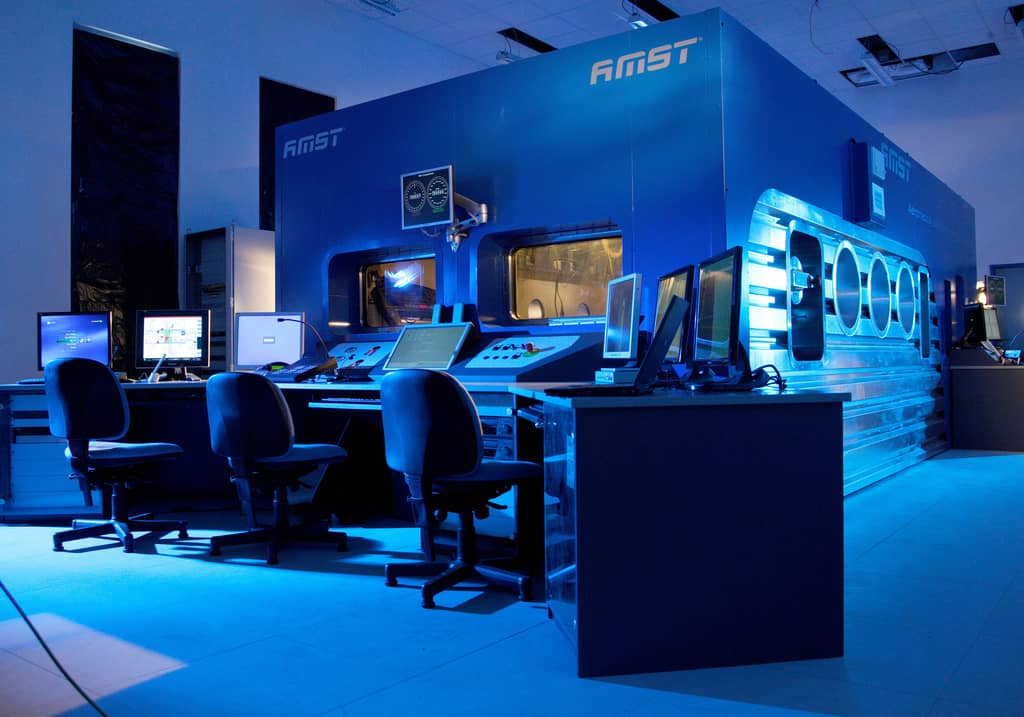
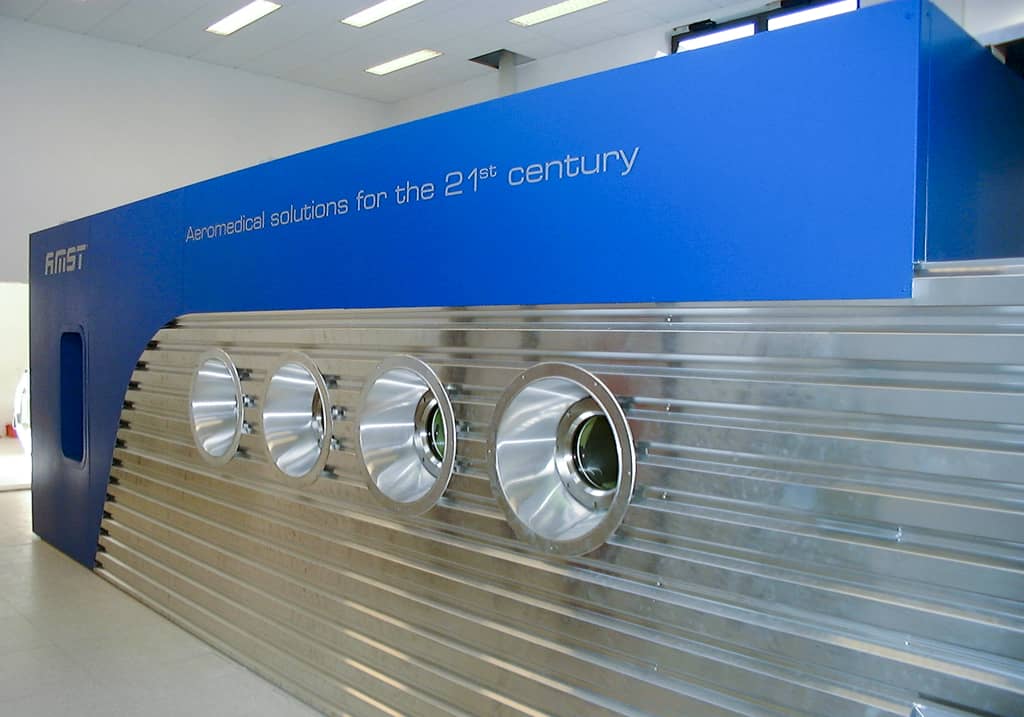
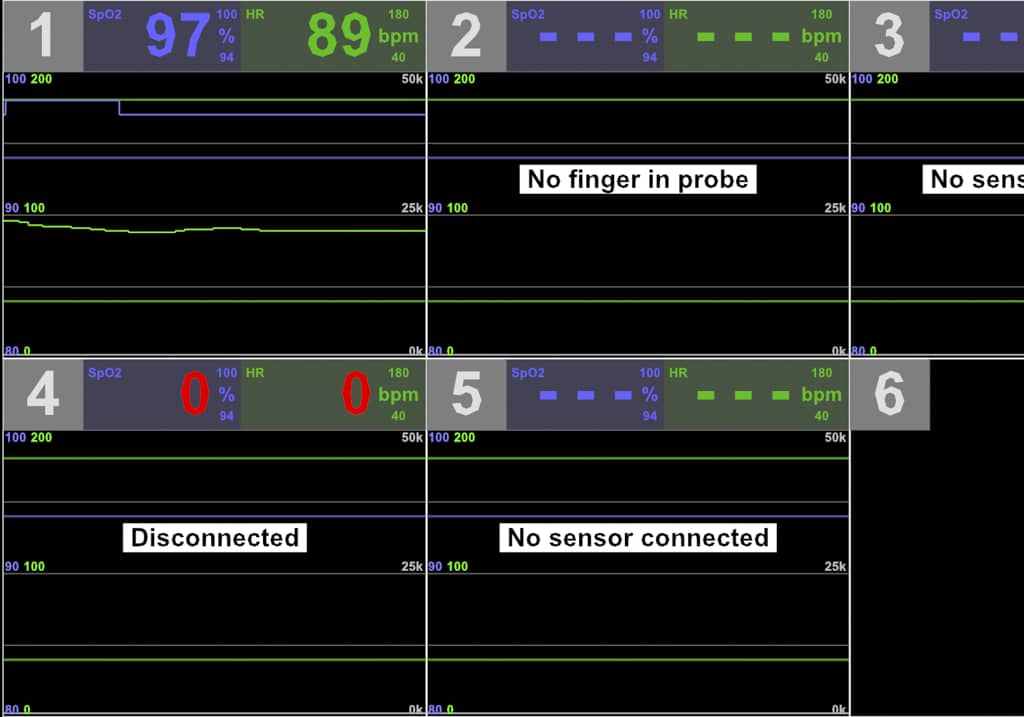
Safety System
AMST’s safety team has long-term experience with international safety standards like MIL- or DEF-standards. They also consider all aspects from previous incidents or accidents which occurred on other suppliers’ products until today. Input from our customers how to improve their operational capability is considered and highly appreciated.